Environment
Geophysical methods are non-invasive, so in addition to generating the least surface damage during the survey, they can also give much more comprehensive information than direct methods, such as monitoring wells.
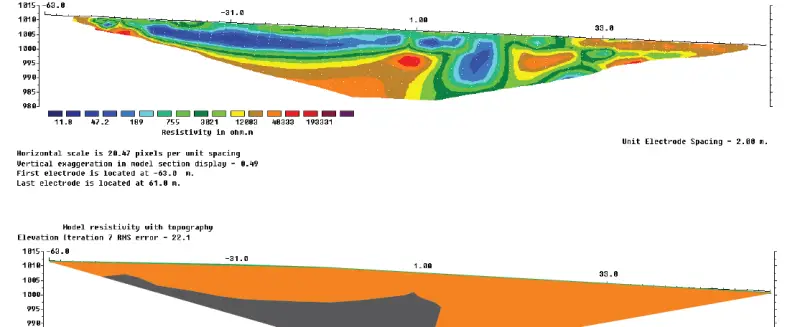
Geophysical methods are a strong tool for environmental studies such as:
- delimit waste deposits (as the example below);
- delimit plumes of contamination and define the probable location of its source;
- to locate structural voids in subsurface and meticulous features;
- contribute to the analysis of possible landslides in slope areas;
- analysis of salt wedges along coastal areas;
- archaeological research;
- among others.
Among the methods used are resistivity, induced polarization (IP), ground penetration radar (GPR) and magnetic field. The variations between each method depend on the depth to be studied (from cm to hundreds of meters), the geological configuration, the possible contaminant, the surface limiters, among others.